disease development
refer to.According to statistics, cervical osteochondrosis is more common in patients aged 25-40 years. This is due to a massive reduction in physical activity and sedentary work. Women are more likely to be diagnosed with the disease than men because their vertebrae are more fragile and their bone tissue is thinner.
- Stage 1– The intervertebral disc loses some of its moisture, its height decreases, and cracks may appear in the annulus fibrosus (shell). This is the stage of cervical chondrosis, which can be difficult to identify because there are no obvious symptoms. The neck will tire quickly, and the damaged area will feel uncomfortable, heavy, and sometimes slightly painful, but it will pass quickly.
- second stage– Increased cracks in the disc surface, and the nucleus pulposus (the gel-like contents of the disc) moves and may protrude from the damaged area. This is how a cartilage-lined protrusion occurs, compressing the spinal cord and its roots. Periods of severe pain, weakness, limited movement, and possible numbness of the face, neck, shoulders, and arms.
- The third phase– The herniation breaks through the outer shell of the disc, causing a hernia. Pain becomes more pronounced and neurological disorders develop.
- Stage 4– The intervertebral disc is almost completely destroyed, the vertebrae rub against each other, and bony growths (osteophytes) appear on their edges, the purpose of which is to stabilize the damaged segment. Nerve endings, spinal cord, and blood vessels are affected. Adjacent joints begin to become damaged. The clinical symptoms are obvious.
reason
- Disrupts metabolic processes.
- Passive lifestyle.
- Genetic susceptibility.
- Chronic muscle tension around the neck.
- Posture is distorted.
- Lack of water and nutrients in the body.
- Remaining in an uncomfortable position (neck stretched forward, back hunched) for long periods of time.
- Being overweight.
- Wear high heels often.
- The store was injured.
- Lift something heavy.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Constant stress, chronic fatigue.
- Low temperature.
- Infectious diseases.
- The neck is too long or too short, etc.
important.The main cause of cervical osteochondrosis in women is menopause and the changes associated with this period. During this stage, the concentration of progesterone in the body decreases, which is very important for bone tissue. The possibility of degenerative changes is related to age-related weakening of the neck muscles and weakening of the vertebral support in the area.
symptom

- Cervical pain occurs when nerve endings become irritated by fragments of damaged cartilage lining. There is then a specific tightening sensation in the neck, and the pain becomes more pronounced when moving the head and after sleep.
- Scalene syndrome is the result of vascular and nerve damage to the brachial plexus and subclavian artery. This symptom complex is accompanied by pain from the inner surface of the shoulder on the injured side to the hand. The limbs become pale, cold, swollen, and numb. When the patient turns his or her head, the neck pain may extend to the back of the head.
- Humeral periarticular syndrome - dystrophic changes affecting the tendon fibers surrounding the shoulder. Pain radiates from the neck to the shoulders and shoulder girdle. The neck has a forced position - tilted toward the affected side, with the shoulders slightly lowered.
- Vertebral artery syndrome - blood vessels become compressed by damaged disc fragments or osteophytes (depending on the stage of the disease). Patients experience dizziness, headache, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. The pain is concentrated in the back of the head, top of the head, and temples.
- Heart-spinal nerve tracts damaged. Heart pain and arrhythmias occur. If C3 is damaged, patients will experience symptoms such as pain in half of the neck, swelling of the tongue, and the inability to chew food normally. If C4 is injured, discomfort will occur in the shoulder girdle, collarbone, and heart area. When C5 is affected, the pain response spreads from the neck to the shoulder girdle, the inner surface of the shoulder. C6 irritation can cause pain from the neck and shoulder blades to the shoulder girdle and spread throughout the arm to the thumb. If C7 is damaged, the pain syndrome can spread to the back of the shoulder girdle, affecting the entire hand, including the index and middle fingers. When C8 is compressed, pain spreads from the affected area to the elbow and little finger.
If the disease persists for a long time, circulatory failure occurs in important centers that perform neuroendocrine functions. Atherosclerosis occurs in the cerebral and cardiac arteries due to increased permeability of the vessel walls.
Create a diagnosis
- X-rays can allow us to detect displacement of the patient's vertebrae, osteophytes on the edges, decreased distance between vertebrae, etc. For this purpose, research is conducted on different planes. To detail the characteristic changes, the doctor will take targeted photos.
- Cervical spine CT scans provide detailed information about pathological changes in the vertebrae. This method allows you to acquire three-dimensional images for more detailed study; it is used in serious diagnostic cases.
- MRI is used to accurately assess the condition of the soft tissues (nerves, blood vessels, ligaments, muscles) in the affected area.
- Electromyography checks the electrical conductivity of nerve fibers.
Conservative treatment
- take medicine.
- Use orthopedic devices.
- physiotherapy.
- Physical therapy procedures.
- Massage, manual effects.
- Alternative therapies.

- NSAIDs. They will help relieve mild or moderate inflammation and pain.
- Painkillers. relief the pain.
- Drugs that improve cerebral circulation.
- Muscle relaxants help relieve muscle spasms.
- Chondroprotectant. They help stop disc destruction, improve metabolic processes, and speed recovery.
- Magnesium-based medications.
- Nootropics. They stimulate brain function by normalizing blood circulation and have a mild sedative effect.
refer to.For severe pain that is not relieved by oral medications, therapeutic blockade may be used, such as with anesthetic solutions or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Dynamic therapy.
- Magnet therapy.
- Use anesthetics, glucocorticoids, and proteolytic agents for electrophoresis.
- Electrical analgesia.
- UV irradiation, etc.
Surgery
lifestyle advice
- Take a walk every day and avoid explosive activities such as running and jumping.
- Do not carry heavy objects.
- You cannot sit for long periods of time; in extreme cases, wear a corset and assume a horizontal position regularly.
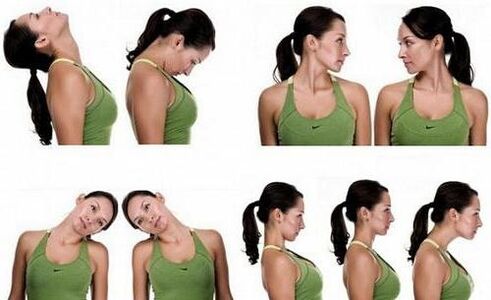
- Perform special physical exercises for the back muscles at home.
- Sleep on an orthopedic mattress and special pillows.
- Follow dietary habits and supplement foods rich in magnesium and calcium (nuts, dairy products, seafood, beans) as well as plant fiber and chondroitin (aspic, jelly). Avoid greasy, fried, salty foods and alcohol. Your doctor will advise you on nutritional rules in more detail. But no matter what, it has to be right.
Hypothermia should not be allowed; warming up without inflammatory processes will be beneficial.
complication
- The possibility of herniation, over time, turning into a hernia. The bulge compresses the spinal cord and its nerves, causing neurological disorders.
- Osteophytes occur when the discs are severely damaged and irritate the spinal nerves and blood vessels.
- In advanced cases, the neck muscles may be severely weak or incompletely paralyzed, and the head may then involuntarily drop to one side or forward.
- The vertebral artery becomes compressed and blood circulation in the affected area is impaired. This condition can cause neuralgia (pain along the nerves), hearing and vision problems.
- Paralysis of the hand (incomplete or complete).
- Stroke, etc.
Precaution
- Evenly load the spine, for example, by placing weights on both hands or alternating weights on the right and left hands.
- Don't lift too much weight alone.
- Try to avoid neck injuries and hypothermia.
- When working in the garden, take a break every 1. 5 hours and lie down for 20 minutes.
- Choose shoes with flexible soles to reduce the impact of running or jumping.
- Use a high-backed chair with a headrest or wear a corset when sitting for long periods of time.