Frequent dizziness, ringing in the ears, flies in front of your eyes, and heaviness in the back of your head are not only caused by fatigue. Usually they are caused by degenerative dystrophic changes in the spine. Headaches in cervical osteochondrosis are typical of the disease. It is impossible to get rid of them without affecting the root cause in the long term.
mechanism of disease development
The degeneration of cervical intervertebral cartilage and bone tissue already causes clinical symptoms at an early stage. Growth and displacement of vertebral fragments inevitably lead to impaired blood flow, innervation, and dystrophy of brain structures.
The causes of spinal deformities in the neck region are:
- Congenital disorders of bone structure;
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar or thoracic spine.
In almost half of the cases, the pathology occurs in young and middle-aged people, and it is more common in women. Its development is facilitated by chronically incorrect head positions during sleep, sitting at desks, telephone conversations and vehicle travel. The habit of sleeping on high pillows also accelerates the progression of osteochondrosis. The mobility of this part of the body, the smaller vertebrae compared to other departments, the location of a large number of large blood vessels and nerve trunks, lead to the early onset of symptoms. Pain syndrome is the main one.
Fragments of the collapsed disc and altered vertebrae compress the vertebral artery and the surrounding plexus. Prolonged compression causes the lumen of the blood vessel to narrow, slowing blood flow and reducing the oxygen supply to the tissue. Osteophyte compression on neural trunks exacerbates malnutrition, hypoxia, and subsequent cerebral ischemia-radiculopathy.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
In most cases, headaches and other pathological symptoms are secondary or vertebral in nature - they are not caused by pathological processes in the brain, but in the adjacent spine.
Reflex headache - boring pain. Occurs when the first three vertebrae are affected. It starts in the upper part of the neck, spreads to the occiput and parietal lobes, and then covers the temples and forehead. It is usually unilateral and resembles a typical migraine. It lasts from half an hour to several days and is aggravated by tilting or turning the head, active physical activity.
Neck and arm pain can occur if osteochondrosis affects the fourth and fifth vertebrae. Its danger lies in the resemblance to a heart attack. The pain is unilateral, sharp, and burning, covering the neck, shoulders, and under the shoulder blades, in the flanks, and sometimes in the forearms and hands.
Myofascial dysfunction causes so-called cervical migraines. A throbbing or compressive pain from one side of the neck that spreads along one side, covering part of the back of the head, the top of the head, the temples, and to the brow arch.
In severe cases, other symptoms are observed: photophobia, red eyes, nausea, weakness.
Osteochondrosis of the neck can cause various types of vegetative vascular dystonia:
- frequent headaches;
- Violation of thermoregulation, intracranial pressure, respiration;
- Sudden mood change.
Speech disturbances, numbness of the tongue, and loss of sensitivity of the fingers can occur with significant compression of the spinal nerves. A person becomes like a drunk or under the influence of psychotropic drugs: he has slurred pronunciation and does not immediately respond to addresses addressed to himself. In advanced cases, tissue dystrophy and impaired blood supply lead to persistently elevated intracranial pressure, vision and hearing loss.
Some facts about this disease:
- Osteochondrosis of the neck occurs about the same frequency in men and women.
- Most of the time, people aged 30-60 get sick.
- Often, morbidity occurs with people who have to constantly be in the same position and perform monotonous movements at work.
- The cervical spine has some structural features, so the disease can manifest in many different ways.
What features of the cervical spine cause symptoms of osteochondrosis?
- The lateral processes of the vertebrae have openings - the carotid arteries pass through them on the left and right sides to supply blood to the brain.
- In the neck area passes the initial part of the spinal cord - it contains fibers that transmit nerve impulses to various parts of the body, providing movement, sensitivity. If the spinal cord in the neck is compressed, neurological disorders can occur throughout the body.
- This part of the spine is highly mobile and prone to osteochondrosis (although in most cases the disease still occurs in the lumbar region - which is not only mobile but also bears the greatest load).
- In the neck, nerve roots emerge from the intervertebral foramen to form the cervical and brachial plexuses. They are responsible for the movement of the muscles of the neck, arms, shoulder girdle, skin sensitivity, regulation of autonomic function.
- The first vertebra doesn't have a huge front - the body - it's a bony ring that rests on the teeth - the bone grows on the second vertebra. This allows the head to turn left and right.
Neck pain, headache, weakness, and numbness in your hands are symptoms that should lead you to a neurologist. Expert examination and examination with modern equipment will help to understand the cause of the pathology and take the most effective measures.
Stages and symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
The first target of the disease is the intervertebral disc. Each intervertebral disc consists of a nucleus pulposus encased in a dense annulus fibrosus. During weight bearing on the spine, the nucleus acts as a shock absorber, while the annulus fibrosus holds the nucleus pulposus within the spine.
With blood circulation and malnutrition, the disc tissue begins to break down. The fiber loops become loose, and the core loses some moisture, becomes thinner, and partially loses its shock absorbing properties. As a result of these changes, the disc has a reduced ability to carry loads and is damaged.
One of the main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis is a shooting nature of neck pain, burning, stabbing, similar to "discharge". It usually extends to one or both hands.
Some patients complain of pain or persistent pain, and in addition to soreness, stiffness of movement, dizziness, headache, and memory disturbance.

In many ways, the nature and severity of pain, and accompanying symptoms, depend on the stage of osteochondrosis:
- 1 stage.Changes occur inside the disc - the nucleus pulposus moves and begins to stimulate nerve endings. But initial pain usually occurs only with physical exertion, exercise, coughing, and sneezing, and you may not feel any discomfort at rest.
- 2 stages.The annulus fibrosus loses its ability to fix the nucleus pulposus, the distance between the vertebrae decreases, and they move relative to each other. Due to these changes, nerve endings may be pinched, causing severe pain. Pain, in turn, forces a person into forced postures.
- 3 stages.The annulus fibrosus is destroyed and an intervertebral hernia occurs. During this phase, the cervical spine is often deformed - its natural curvature is reduced. The hernia bulge compresses or irritates a nerve root, causing persistent severe pain in the neck and arm, often with numbness and muscle weakness.
- 4 stages.The annulus fibrosus becomes dense and adhesions form between the vertebrae. As a result, immobility occurs in the affected area, and pain may even decrease.
diagnosis
If you complain of poor health with cervical osteochondrosis, you should contact a neurologist. During the exam, the doctor determines the source of the pain. To do this, he used the following methods:
- Pressing the area of the cervical spine where the nerve root protrudes with your fingers: the pain response that occurs indicates a headache;
- Press the point near the bony process below the lower edge of the ear: Pain episodes after this clearly indicate the development of cervical migraine due to mechanical compression.
In order to accurately diagnose cervical osteochondrosis, some instrumental studies are required. Radiography, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are still dominant. With their help, pathological changes that occur in bone, cartilage and soft tissue structures are visualized.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
The drug is designed to eliminate symptoms, restore normal blood circulation, and biomechanics throughout the cervical spine area.
To reduce pain, use NSAIDs, analgesics, muscle relaxants, and antispasmodics.
Vasodilators - Vasodilators help reduce vegetative manifestations, improve venous outflow and prevent edema in the affected area.
Means containing B vitamins and magnesium help to improve the nutrition of nerve tissue cells and reduce adverse symptoms.
At the same time, patients are advised to take drugs that regulate blood pressure and correct heart rhythm.
Many patients take sedatives, antidepressants, sedatives.
Depending on the severity of the condition, the course of treatment can be long or short. Painkillers are used once or for a few days. Means of normalizing blood flow and vitamins - a 2-3 month course.
To maintain the effect of the drug, physical therapy is prescribed:
- Collar area massage;
- Acupuncture and Reflexology.
The wearing of a therapeutic bandage to support the neck muscles is shown as the condition worsens.
In the absence of worsening osteochondrosis, therapeutic exercise can help stop and prevent the symptoms of VVD. Gymnastics help strengthen neck muscles, relieve spasms, and improve the elasticity of blood vessels and ligaments of the vertebral joints. Training includes soft tissue stretches: deep head tilts, turns, rotations.
Patients with osteochondrosis and VVD should arrange their sleeping places carefully. You just need to rest on an orthopaedic mattress and pillow and don't drink a lot of fluids at night to avoid swelling. It is necessary to avoid jobs and hobbies related to the unfavorable position of the cervical spine: leaning back or tilting the head low.
All materials provided on the website are for educational purposes only and are not intended for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. The site administrators, editors and article authors are not responsible for any consequences and losses that may arise from the use of the site materials.
Cervical osteochondrosis dizziness
Dizziness from cervical spondylosis is common in both men and women, starting at age 30 and older. The particularity of lifestyle and some abusive behaviors cause almost every second of our residents to develop cervical osteochondrosis in adulthood. Some patients already have problems during adolescence.
It is impossible to underestimate the danger of this pathology: it can worsen one's well-being and lead to the development of dangerous conditions. Its symptoms are various unpleasant sensations.
Causes of dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis
In the article, we will consider whether cervical osteochondrosis is chronically dizzy and sick, why it happens, what to do as the condition worsens, and how to get rid of the discomfort forever.
The condition of the spine in this area is gradually changing due to a less healthy lifestyle and frequent overloading of the neck area.
Degenerative changes occur in the intervertebral discs, and the spinal nerves and blood vessels supplying the brain gradually narrow through these holes.
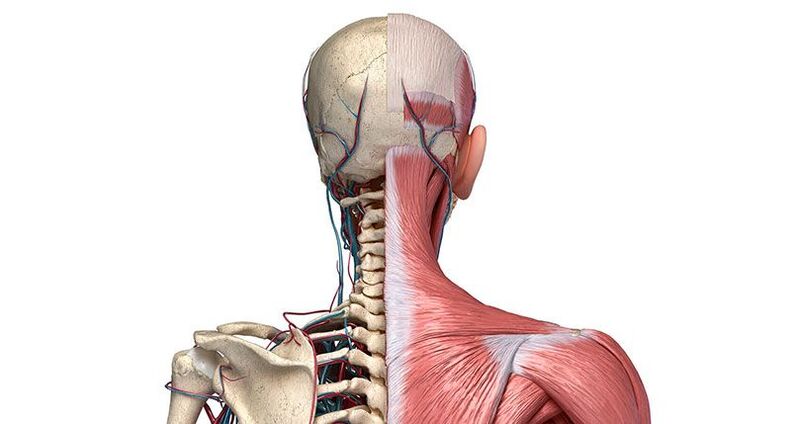
This situation is very unpleasant and dangerous. The patient experiences pain when suddenly moving certain parts of the head and neck. The brain receives less oxygen than it needs, which can trigger frequent dizziness.
The main reasons why people with osteochondrosis may feel dizzy:
- Bone growth compresses the vertebral artery. Osteophytes can clamp on blood vessels that supply the cerebellum and the basal part of the brain. Its permeability is reduced, reducing the amount of blood and oxygen passing through it. In medicine, this phenomenon is called vertebral artery syndrome.
- Frank's nerves were stimulated. The nerve fibers of the sympathetic nervous system wrap around the vertebral arteries and feel any influence on it. In response to stimulation, the nerve causes vasospasm, impairing its patency. Hernias, osteophytes that form, or instability of the cervical spine can cause discomfort.
- Subluxation of the superior articular processes of the lower vertebrae or the formation of a herniated disc in the neck area.
Dizziness and nausea caused by cervical osteochondrosis, as well as the manifestation of other symptoms, such as female weakness, drug treatment is necessary, but what to eat, what medicine to take will help, only the doctor will decide to study the patient's condition in depth later. After all, the causes of dizziness are varied.
Various means and techniques are used depending on the specific cause of the pathological condition and the development of negative symptoms.
You need to understand that dizziness is a very dangerous condition if the episodes intensify and become frequent. Not only can a person be life-threatening by driving or crossing the road, but they can also be at risk of encephalopathy because neurons are often starved of blood and nutrients.
other symptoms
Before deciding what contributes to the appearance of dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis and what exercise can prevent unpleasant episodes, you should not read reviews from strangers, but rather evaluate the accompanying symptoms that develop during the course of the disease.
Based on these signs, an experienced doctor will suggest the degree of development of the osteomalacia. It is also capable of assessing the risk of the condition and compiling diagnostic algorithms. Then - choose an effective and safe treatment.
Symptoms that accompany decreased carotid patency and indicate the need for urgent medical consultation:
- Intermittent tinnitus, which may be pulsatile. Then gradually spread to the entire head. Typically, seizures occur in the context of being in an uncomfortable position, physical exertion, or severe fatigue.
- Cracking, pain when moving neck.
- When the head is tilted back, the eyes darken and there is a brief faint. In advanced situations, even sharp turns can cause this reaction.
- Nausea, up to vomiting, with episodes of dizziness.

Is the head turning not a cervical spondylosis, why it occurs, and what to do, only a neurologist will tell you after the examination. The sooner a diagnosis is made and treatment begins, the more effective the measures taken.
If you seek help early, you have a chance to avoid medication and get rid of problems that have already developed. Delaying a visit to the doctor risks triggering the development of a more dangerous condition.
diagnosis
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis with dizziness, what to do if there is a motor coordination disorder, and what medicine to prescribe in this case, you can figure out after a thorough diagnosis, as each case is unique.
Before deciding on a treatment plan, it is important for doctors to identify the factors that influence the development of the disease. It is necessary to clarify how quickly it deteriorates and what are the characteristics of its process. Because of these features, a thorough diagnosis is made when dealing with complaints of recurring dizziness.
A neurologist performs an initial examination, during which:

- Determining the range of symptoms that accompany the disease process;
- According to the results of the physical examination, the characteristics of changes in the neck region were found;
- Collection of medical records, history of disease development;
- Ask patients about their life characteristics to identify risk factors that influence disease development.
After that, an instrument check will be scheduled:
- MRI of the brain and neck to determine if changes have occurred and the extent of changes;
- Ultrasound of blood vessels through the neck will show how smooth the blood flow and how much nutrition to the brain has been reduced;
- Cervical spine CT shows deviation from the normative formation of bone structure;
- EMG allows you to record the electrical activity of the muscles in the area being assessed;
What to do if your head spins off your neck and hurts, the correct answer is to see a doctor. The clinic will pinpoint the cause of the poor condition and select the appropriate treatment.
treat
After identifying the specific stage of the disease, doctors prescribe individual treatments. After all, phenomena such as occipital neuralgia can be encountered and need to be treated in their own way.
Prioritize complex treatments, including:
- taking medication (chondroprotective agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc. );
- physical therapy techniques;
- Various massage techniques;
- Physiotherapy sports, a professional complex of sports therapy;
- Follow a healthy diet.
When you feel dizzy due to osteochondrosis of the neck, it can be treated with conservative methods and surgical intervention.
Surgery is performed when the spine is too narrow or a persistent hernia has formed.
Early effective treatments are massage and special exercises. Following the doctor's advice during the preclinical stage of the disease's development can completely cure it.
The results show physical therapy methods that can eliminate painful symptoms in several sessions:
- classical manual therapy;
- How the shock wave affects the body;
- hydromassage;
- Laser therapy.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is a necessary emergency step when the head is already often dizzy.
This dangerous symptom is an indicator of the development of a truly dangerous disease that can further deteriorate the comfort of human life. even shorten its duration.
prevention
With the help of regular preventive measures, the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms can be prevented or their severity can be significantly reduced. Many people are wondering, is it effective to use painless money for dizziness caused by cervical osteochondrosis, and how to get rid of it and relieve the attack quickly, instead of treating it at home?
lifestyle prevention
We list appropriate measures to prevent disease progression:
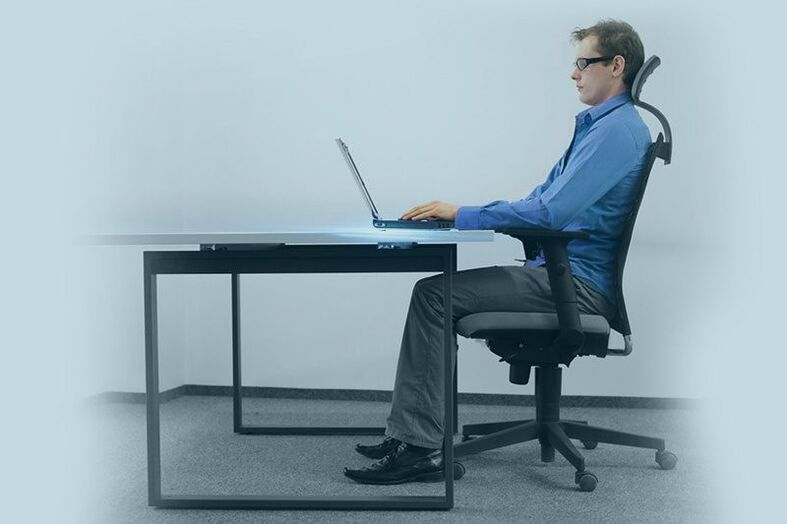
- Reduce time spent in curved positions. For example, at a computer, gadget, or job that requires neck tension and a forward head tilt. Provide an ergonomic workplace.
- Organization of alternate systems of work and rest.
- Rejecting Habits, Destructive Addiction. The amount of drinking and smoking needs to be reduced.
- Set a place to sleep. Purchase orthopedic pillows and mattresses that take into account the structural characteristics of the spine.
- Add physical activity to your daily schedule and avoid physical activity.
- Do regular special warm-ups during the workday. Ideally, you should set aside 5 minutes per hour for exercise.
- Avoid traumatic activities, extreme sports and excessive physical exertion.
- Pay attention to your weight. When obesity occurs, try to lose excess weight as quickly as possible.
- Take regular professional massage classes to learn safe self-massage techniques.
- Use a comfortable backpack to carry things and avoid bags that cause askew when walking. Use a headrest when traveling in a seated position.
- In case of injury, seek help immediately. Follow medical advice from day one.


In the context of preventive measures, an injury to the neck and back of the head is an impossible situation to ignore. This is the first symptom of the disease and requires treatment.
power protection
It is beneficial to follow a special diet that will support the medically induced recovery process of the neck and cervical spine.
Key principles of nutrition in the presence of such problems or susceptibility:
- Use gel foods in food to help restore cartilage in the body;
- Maintain a balance of protein and carbohydrate foods, with moderate amounts of lean meat and fish in the diet;
- Limit excess consumption of salt and spices;
- Reduce consumption of pickled and smoked products;
- A diet that reduces sweets, including rich products;
- Limit caffeinated beverages;
- Increase the proportion of fresh vegetables and fruits in the daily menu;
- Avoid greasy and fried food, fast food.
Exercise therapy should occupy an important place in the lives of people with similar conditions. They are particularly relevant to the elderly or to a sedentary lifestyle. At the same time, in order to achieve the desired effect, a special set of exercises must be repeated every day.

Despite the variety of traditional medicine, dizziness from cervical osteochondrosis, what to do, what to drink, how to deal with flare-ups, how to treat deviations or eliminate specific symptoms, does this or that remedy really help? Inflicting additional damage should be determined by a professional physician. An online consultation with a neurologist can help here.
Don't blindly follow a friend's advice and try to eliminate the disease without getting the advice of a qualified doctor.
In advanced cases, osteochondrosis not only reduces quality of life, but also deprives a person of the ability to work. Therefore, try to pay attention to the factors that may lead to the destruction of the intervertebral disc in time and eliminate or reduce its harmful effect on the spine as much as possible. If you are concerned about neck pain, be sure to consult your doctor. Only a specialist can determine the stage of the disease, choose pain relievers and prescribe physiotherapy exercises or courses.